|
Intersections
|
|
Intersections
|
This command allows for the calculation and storing of points based upon standard surveying practices of Bearing-Bearing, Bearing-Distance, or Distance-Distance Intersection calculations. Data can be entered manually, or defined by selecting points from a point list or selecting points from the screen. The kind of intersection calculation to be performed determines the number of possible solutions. With a Bearing-Bearing calculation, there will be only one possible solution. Bearing-Distance, and Distance-Distance calculations will have two possible solutions prompting the user to pick the desired solution. Note that in intersection calculations of Bearing-Distance and Distance-Distance there may be no solution for the input data. In these cases, Carlson SurvCE will display the message, "No Valid Solution".
From the COGO Menu, select Intersections. Fill out the appropriate data fields to perform the desired calculation. The Enter key moves forward through the edit boxes. The current Angle setting in Job Settings, Units, dictates whether angles are prompted as azimuth or bearings.
All Intersect routines create SP records in the raw file, storing the calculated coordinates for each new point. This SP record is identical to records created by Keyboard Input, for example.
Bearing-Bearing
This method locates a point at the intersection of two lines. Select Point 1 by entering directly the desired point number, or pressing the point list icon and selecting the desired point. Pressing the map icon will allow for selection of the desired point directly from the screen. Note that when picking from the screen, if the desired point cannot be determined from the picked point on the screen, a listing of the nearest points to the picked location will appear allowing for verification of the desired point. If the list appears, select the desired point from the list by clicking on it.
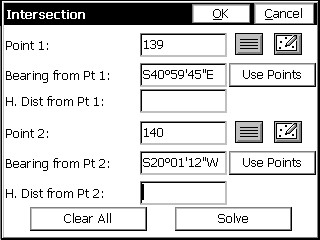
Define the bearing from point 1 by typing in the bearing, or by selecting Use Points, and defining the bearing by specifying two point numbers or select the map icon and selecting two points from the screen. Repeat the above procedures for selecting point 2 and defining the azimuth from point 2. Bearings can be entered in 3 forms:
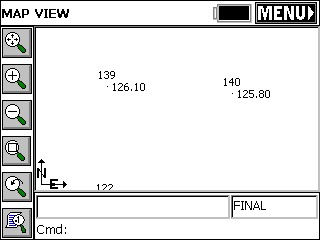
Once data entry is complete, press solve button. The calculated point will appear on the screen with the input data detailed at the bottom of the screen. Store, Modify (review and revise) and RESULTS Options are located on the right side of the Map screen. Press S to store the calculated point, press M to verify/revise calculation input data, or RESULTS to review the calculation results. The results screen will display the coordinates of the base points, the inverse bearing and distance from the base points to the calculated INT1 point (and INT2 for distance intersections) and the coordinate data for the calculated points. Note that calculated points are labeled as Int1 and Int2 until the points are stored. These Option Buttons are present on all Map screens displayed while in the Intersections routine. Once store is selected or the enter key pressed the stored point will inherit the specified point number, description and optionally the elevation displayed at the bottom of the screen. There can be only one solution for a bearing-bearing intersection. The first figure below shows the two original points. The figure below it shows the intersection dialog with values filled in.
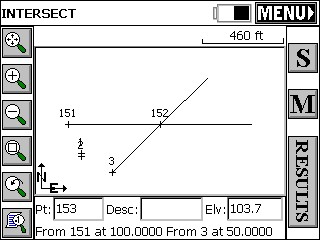
All Intersect routines handle the 400 circle, if configured to grads/gons within Job Settings, Units. Shown below is the intersection of a 100 gons (due East) azimuth from point 151 and a 50 gons (northeast) azimuth from point 3.
Bearing-Distance
This example uses the same two base points as shown in map screen above. Select Point 1 by entering directly the desired point number or press the point list icon and select the point by clicking on the desired point. Pressing the map icon will allow selection of the desired point directly from the screen. Define the Bearing from point 1 by typing in the bearing, or by selecting Use Points, and defining the bearing by specifying two point numbers or select the map icon and select two points from the screen. Select Point 2 using the same methods as Point 1. Enter the known horizontal distance from the selected point 2.
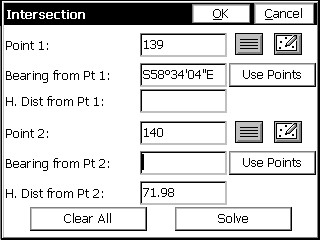
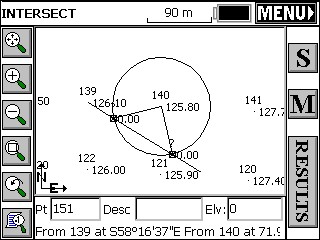
Press enter, or tap the solve button, and the map screen will display, showing a circle radiating from the selected distance base point. A line defined, by the bearing, is extended to intersect the circle at the two possible calculated solutions. See the next figure.
Pressing enter will display the prompt "Pick a Solution". Select desired calculated solution. To select the point simply pick it from the screen. Picking near the desired solution is sufficient. The program will select the nearest solution position. Pressing enter again will accept the the second possible solution for the intersection. To accept only one of the possible two solutions, select the desired point and then press the menu button at the top left of the screen. If there was no solution for the input data, SurvCE will display "No Valid Solution". Pressing OK will display the map screen showing the circle radiating from the distance base point and the line defined by the bearing input. The map screen displays the options of S (Store), M (Modify) and Results. Press M to do a new calculation. If there is no valid solution, pressing the results button will display only the base point coordinates.
Distance-Distance
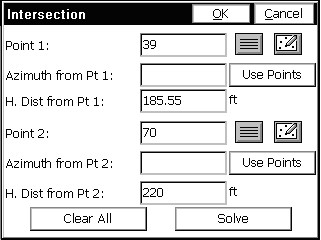
This example uses the same two base points as shown the map view screen shown in Bearing-Bearing. Select Point 1. Enter the known horizontal distance from Point 1. Select Point 2. Enter the known horizontal distance from the selected Point 2.
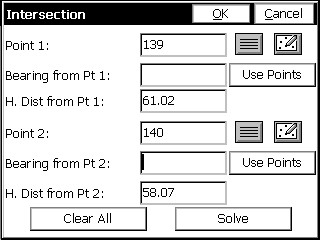
Press enter or tap the Solve button and the map screen will display showing circles radiating from the first and second selected base points. See the next figure. Lines leading from both base points to the two possible intersections of the circles are also shown.
Pressing enter will display the prompt "Pick a Solution". Select desired calculated solution. To select the point simply pick it from the screen. Picking near the desired solution is sufficient. The program will select the nearest solution position. Pressing Enter again will accept the second possible solution for the intersection. To accept only one of the possible two solutions, select the desired point and then press the menu button at the top left of the screen. If there was no solution for the input data, SurvCE will display "No Valid Solution". Pressing OK will display the map screen showing the circle radiating from the distance base point and the line defined by the bearing input.
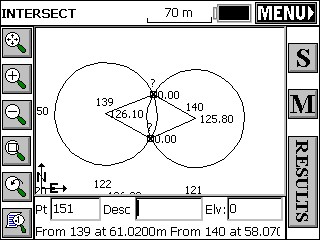
On the map screen display the options of S (Store), M (Modify) and Results are present. The M option can be used to revise the existing data or enter new data for the intersection calculations. If there is no valid solution, pressing the results button will display only the base point coordinates.